•
20-minute read


SEO industry changes, and so do SEO best practices and techniques. In this post, I’m showing you the top SEO practices to bring your site to the top of Google in 2023.
Ready? Let’s go.
Google has to properly see and understand your site to rank it. So, the first thing you should focus on is technical SEO.
The best way to directly notify Google about your new pages or site changes is to directly request indexing via Google Indexing API.
To start using the Indexing API, you need to activate the API in Google API Console and create a service account for your further work (mind that you have to grant your new account an owner status).
You will also need to verify ownership of a new service account in Google Search Console by adding the newly generated service email as a site owner.
Back in Google API Console, generate a key for your new account, like this:
Once you’re all set, you can send requests to notify Google about your new pages. You can add (or exclude) a single URL or a set of pages (in this case, collect them in a .csv file) with the help of scripts — for example, this one will do.
If your site is running on WordPress, things are a bit easier — there’s a plugin to help you get all the Indexing API routine covered.
As you can see, this practice requires some coding skills, so you can hand the manual work over to your webmasters if you don’t want to bother with Python. Alternatively, you can try generating a script with ChatGPT — give it a task as if you were giving it to a human developer.
A site structure is considered good when it is shallow. This means that all the end destination pages should be not more than three clicks from the homepage.
If the destination pages are located too far, then these pages may have indexing problems. The thing is actually that Google crawlers draw parallels between the depth of the page and its importance, so if a page is located deep, it is then considered less important. Thus it is less likely to be recrawled on time and appear in SERPs.
A shallow site structure also lets you add new pages without affecting the overall site structure and click depth, so you will have enough room for new content.
Tip. Use the Click Depth column of WebSite Auditor to quickly understand the click depth of your pages.
Redirect issues may prevent your pages from getting link juice and even from being indexed. To avoid this, make sure your redirects are set up correctly and confuse neither Google nor your visitors.
The key thing to consider here is the topical relevance of the pages you redirect — for example, a page about tomatoes cannot be redirected to a page about cucumbers. Google will not make any connections between the pages’ content and may treat such redirects as soft 404s.
It is interesting that John Mueller has recently said that redirects from non-relevant pages don’t cause the destination page to be less relevant:
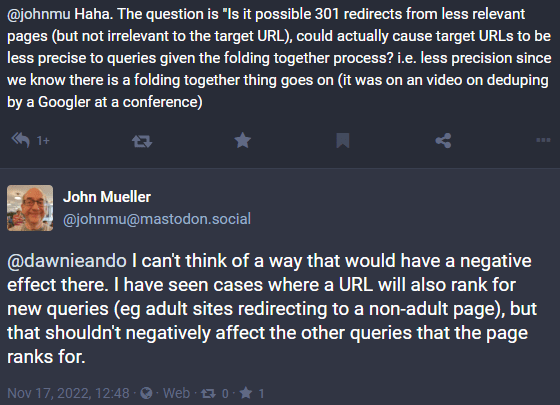
But this statement contradicts his own words from the Google Webmaster Central office-hours video hangout where Mueller says that “the 301 redirect from all pages to the home page, that would be something that we see as a soft 404s.”
You can say that the video is pretty old and things may have changed, but here’s a real-life example. A strong page was redirected to a new and weaker topically irrelevant one to boost its positions, but the new page lost positions instead of growth:
On this graph, the traffic drop correlates with the time when topically irrelevant redirects were implemented. When the issue was fixed, clicks grew back again.
And here’s how a topically relevant redirect may influence your page’s position and traffic:
On our blog, we have a detailed guide on how to carefully set up redirects — feel free to consult if for in-depth guidance.
As for the best recommendations on redirects themselves, use 301 redirect to inform Google that your page has been moved. Also, avoid long redirect chains, as they make it harder for Google to discover the destination page, plus drain PageRank.
All the pages on your site have to be well-linked so Google can discover them when crawling your website. Because if a page is hidden in a redirect chain or is not linked at all, it will just sit idle and bring no use.
To help Google and users discover your pages and increase visibility, set up a navigation menu that contains all the necessary pages. In the graph below, you can see how adding one of our pages to the menu helped improve visibility:
Besides, wise internal linking helps allocate PageRank and boost the pages you need. In addition, internal linking helps Google establish logical ties between pages and, consequently, between topics. In this regard, pay attention to anchor texts — they should clearly demonstrate the key idea of the page they lead users to.
Tip. I often come across discussions around footer links. People argue if they (links) are useful or not.
So what’s the answer? It’s our “favorite” it depends. Footer links are usually utilized to help users and search bots navigate across the website, especially if some links are not present in the navigation menu for any reason. What is also true is that footer links do not do any harm to your site, so it’s up to you whether to use them or not.
Slow pages bring nothing but low positions and high bounce rates. Moreover, Google is likely to fail to see the content of the page and consider it empty or cloaked, which is a direct way to a penalty or even delisting.
To fix PageSpeed-related issues, make sure your pages load quickly and pass the Core Web Vitals assessment.
You can check your pages in Google’s PageSpeed Insights and Search Console, or do the bulk check in WebSite Auditor. All these tools provide fix suggestions, so you will see the opportunities for improvement.
One of the main causes of PageSpeed issues is heavy images, videos, design elements, etc. In the era of visual perception, having good-looking visuals is a must for your website. Still, don’t overdo:
Don’t use heavy visual elements within the viewport — they are hard to load and don’t let Google see the content behind them;
Do not overuse abusive pop-ups — they prevent Google from quickly loading the page and annoy users;
Get rid of unnecessary JavaScript which is heavy — Google cannot render it, so your page may be considered empty;
Clean up your site code to remove legacy elements — you may not need them anymore, still, they waste loading resources and slow the page down;
If you use a CMS, be careful with plugins — although they are meant to help you, they also slow the site down. Make sure you only keep the necessary ones or choose a CMS which is SEO-friendly out of the box.
As Google moved to mobile-first indexing, having your site optimized for mobile devices is a must. Besides, millions of users do choose smartphones over PCs just because they are always at hand and let access information anytime.
As for the top solutions for mobile SEO, make your site design responsive so it would fit any device. Don’t overdo it with viewport-blocking pop-ups and ads — they make UX a disaster and may even get you under Google penalty for misleading content if search bots fail to read the content behind the pop-up. In addition, take care of font size so the text is readable.
If you use a CMS, choose a responsive site template — designs like these have in-built features to serve users on any type of device, so you will have less headache about mobile usability.
To see if your site is suffering from any mobile-related issues, check the Mobile Usability report in Google Search Console.
If you plan or already have international site versions, then make sure you handle everything to avoid localization issues. One of the problems international SEOs and site owners face is how to strengthen the newly-created localized versions and connect them to the original domain.
While interconnection is handled with the help of hreflang setting and specification, spreading link juice may turn out to be a more complicated thing.
Thus, think carefully about how to set up your local site versions — as a separate domain, a subdomain, or a directory. Which one is the “best”? As you may have guessed, it depends. It depends on your business peculiarities, legal procedures, and how much all of that affects the content of your pages.
Still, remember that if your primary goal is to pass some link juice to new pages, then creating directories is the only option, as your already strong domain will help boost new pages. Sometimes having international versions as directories is not an option. In this case, you need to properly interlink your new site versions with the main one to make these links work like backlinks and give PageRank to newly built pages.
Backlinks are crucial for SEO. Although Google is trying to persuade us they’re not, SEOs have proved their importance many times. Besides, Google would have not introduced so many updates and link regulations if this factor was a really minor thing.
So here are the ways how to equip your website with high-quality backlinks without the risk of getting a penalty from Google.
One of the best ways to get relevant and authoritative backlinks is to find backlink prospects who work with your competitors.
First, if a provider links back to several competitors, then chances are they will link back to you. Second, a prospect like this is surely relevant to your niche and trusted — your competitors have already proved this.
A nice way to find relevant prospects is to analyze your competitors via SEO SpyGlass (Domain Comparison > Link Intersection > Prospective Domains).
Download SEO SpyGlassPay attention to the Domain InLink Rank column and check if provided links are dofollow, as they are what you’re looking for.
Outreach prospects and get the details of the backlink partnership.
Placing a guest post on a credible resource is a great way to build links, boost brand popularity, and prove expertise.
Reach out to relevant sources to get more details on post placement. For example, some websites offer a list of topics they need, while some ask you to offer the topic first. Agree on the number of links per post.
Provide enough information to include in the author's profile. If possible, add some links that prove expertise, mention professional achievements, share if the author participated in conferences — all of that demonstrates expertise and strengthens E-E-A-T signals that also matter when it comes to page strength.
There are listicles featuring products and services in any business area, from AI technologies to dairy farms. Do a research to find listicles for your niche and connect with their authors to add your product there.
Tip. You can use LinkAssistant to find listicle inclusion opportunities in bulk. The tool will show the relevant pages according to the set of preferences, demonstrate the preview of the page, and tell if that page mentions your competitors.
Your backlink prospects may be closer than you think — just look at the list of your business partners, clients, providers, etc. They are very likely to mention you on their pages in reviews, listicles, or happy clients sections.
If you operate a local business, try to get mentions from the neighborhood businesses. In this case, they may not even be your partners or clients — it is the location that matters. Doing so will help Google build ties between you (a business entity) and the physical area (location entity). The entity-based approach is a key to success in local SEO, so you should not ignore it.
Broken link building is a tactic that lets you find backlinks of your competitors that respond with 404 and try to replace the broken target page with your working one. This method is beneficial to both you and the provider — you get a backlink while they keep providing their users with relevant information.
This is how it works. In SEO SpyGlass, create a project for a competitor’s website and check the Backlink Profile > Backlinks section.
Download SEO SpyGlassCheck what linked pages return the 404 status code (note that you only need to check dofollow links, so set up filters).
Then I recommend manually checking the page that provides a backlink. If you decide that the page is relevant, contact webmasters or the author of the post and suggest replacing a broken link with yours.
Wisely added on-page SEO elements may help you more than you think.
Meta titles and meta descriptions actually help users decide if the page is worth clicking as they are what users see in SERPs.
Still, there’s a tricky issue. These days, Google has a habit of rewriting meta titles and descriptions according to the search query. For example, this is what Google showed as a description of our post about local SEO:
Whereas the actual meta description looks like this:
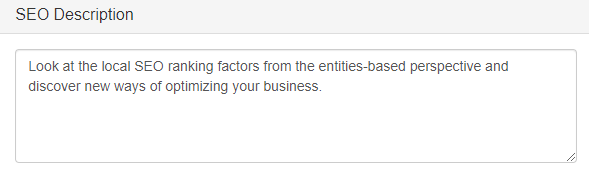
Still, this doesn’t mean you have to rely on Google’s creativity and do nothing yourself.
First, remember to keep your meta elements short — a maximum of 60 characters for titles and 150 for descriptions. This helps minimize the chances of having your meta elements rewritten. Besides, Google is simply not able to display more symbols. Second, place keywords closer to the beginning — again, to let Google quicker see the necessary words and prevent it from reassembling titles and descriptions.
To get some inspiration, check how your SERP competitors manage titles and descriptions with the help of the WebSite Auditor’s Content Audit module:
Download WebSite AuditorStructured data are the way to provide Google with clearer information about your page and win a rich snippet. Rich snippets are catchy and attractive, so they are likely to win more clicks. So, it is clear that you need them.
There are schemas for almost any type of content, be that a recipe or a product page — choose any that suits you and go ahead. Make sure you have chosen the relevant one though; Google may penalize a site for using irrelevant or deceptive schemas.
If you don’t feel like digging through nearly a thousand schemas, use Google Structured Data Markup Helper — its 12 schemas cover most basic needs.
Once everything is tagged, test the page via Google Rich Results Test to make sure all works fine.
Schema markup is the way to give Google information in the most digestible form. The more data Google has, the higher the chances that Google grants your entity a knowledge panel, which occupies a pretty big amount of the SERP.
Descriptive alt texts help Google better understand the content of your images, train Google’s AI, and, as a result, help you get some more traffic with images. Even if image SEO may not be your primary goal, more clicks are never bad.
A good way of creating better alt texts is to upload your image to Google's Cloud Vision API and check what Google already sees on the image.
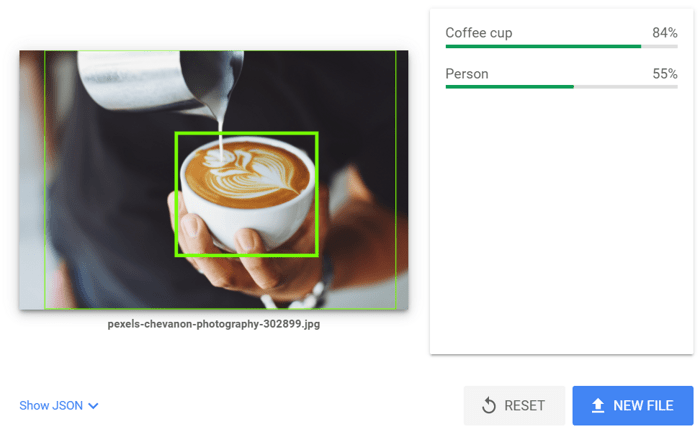
You can then tune the text to make the description more detailed. Alternatively, you are free to change the description completely if Google did not get the content right.
Tip. If you don’t remember if images on your page have alt texts, check the page in WebSite Auditor.
These days, best content creation practices are mostly focused on writing valuable content for people, not search engines. Besides, as AI writing tools become more and more widespread, expertise becomes an issue as well, especially in the areas where real-life experience is of great importance.
In SEO, content has to target the keywords and queries which the page is supposed to be found with. How do you choose the keywords that will suit your page? Sure thing, with the help of keyword research tools, but keep in mind that sometimes simply taking keywords with the biggest traffic potential is not the best idea.
For example, when you search for keywords in Rank Tracker, pay attention to Keyword Difficulty.
Download Rank TrackerIf the keyword is way too difficult for you (at the moment at least), then consider another one. It may have less traffic potential but is easier for you to rank for. Once your site gains more authority and strength, you will have a higher chance to compete for difficult keywords.
At the same time, don’t waste your time and effort on some too easy keywords with super-low traffic potential. Find balance.
Tip. To better understand what keywords to use, check how Google understands your content via Google's Natural Language API (NLP API). The tool will help you check if Google finds the necessary entities in the given piece of content. Depending on what you see, you can add the necessary keywords to help Google see what you actually meant.
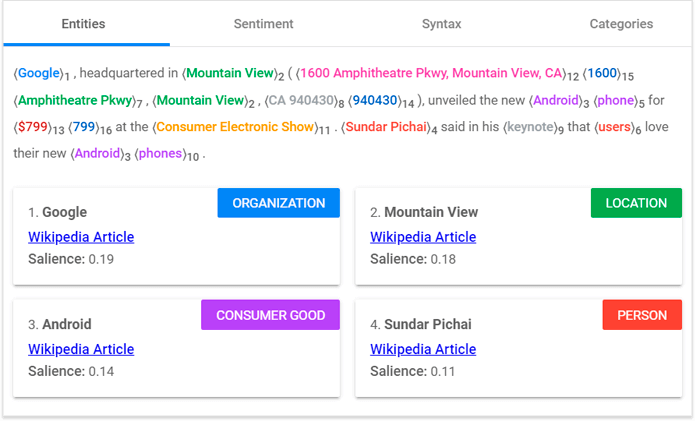
Search intent is what stands behind every search query and actually means the reason why the search was executed for. And it’s clear that a keyword with clearly transactional intent (say, sneakers buy) is not likely to trigger a how-to post or a video. That’s why you need to properly understand the intent of the keyword to get your page to the top of SERPs.
Actually, checking the SERP is the best way to understand the intent behind the keyword and create the right type of content. Say, if a keyword mostly triggers listicles, then you need to write one, too.
In addition, Google can give you a hint on the preferred content type in the following way. Once you conduct a search, look at the Google feature that comes first:
Shopping usually indicates that SERPs will contain product pages, and Maps may signalize that the SERP will feature a local pack and listings like best X places to eat in Malaga.
Tip. Check the Google SERP Features section of Rank Tracker to bulk-check what SERP features a keyword triggers, and what types of content to add to your page to get featured there. Those gray ones are the features you’re not present in yet.
The importance of E-A-T keeps being mentioned in Google content guidelines. What’s more, it has evolved into E-E-A-T where the new E stands for Experience. Experience has become important as people have started using Chat-GPT for content more often than ever, and AI is not likely to have any real-life experience in any topic, no matter how good the text quality is.
Although Chat-GPT may learn new datasets in the future, there’s one thing it will not be able to do — use products and describe its experience. So this is the way to improve your content. Add some examples from personal experience, describe real use cases, and mention peculiarities that can only be revealed in use, not taken from the product description.
The industry of SEO reacts to technological progress and keeps developing accordingly. And, according to where we are going now, these tactics are going to be relevant for at least 2023. If something changes, we will add the new info asap so you can quickly optimize your site using the top SEO practices.
By the way, what was the tactic you benefited from the most? Share your experience in our Facebook community.
| Linking websites | N/A |
| Backlinks | N/A |
| InLink Rank | N/A |